38 coupon value of a bond
Calculate the Value of a Coupon Paying Bond - Finance Train The value of a coupon paying bond is calculated by discounting the future payments (coupon and principal) by an appropriate discount rate. Suppose you have a bond with a $1,000 face value that matures 1 year from today. The coupon rate is 12% and the bond makes semi-annual coupon payments of $60. The bond yield is 13%. What Is the Face Value of a Bond? - SmartAsset A bond's coupon rate is the rate at which it earns these returns, and payments are based on the face value. So if a bond holds a $1,000 face value with a 5% coupon rate, then that would leave you with $50 in returns annually. This is in addition to the issuer paying you back the bond's face value on its maturity date. Bonds are generally considered safer investments than equity investments (stocks). But as with any investment, nothing is a sure bet.
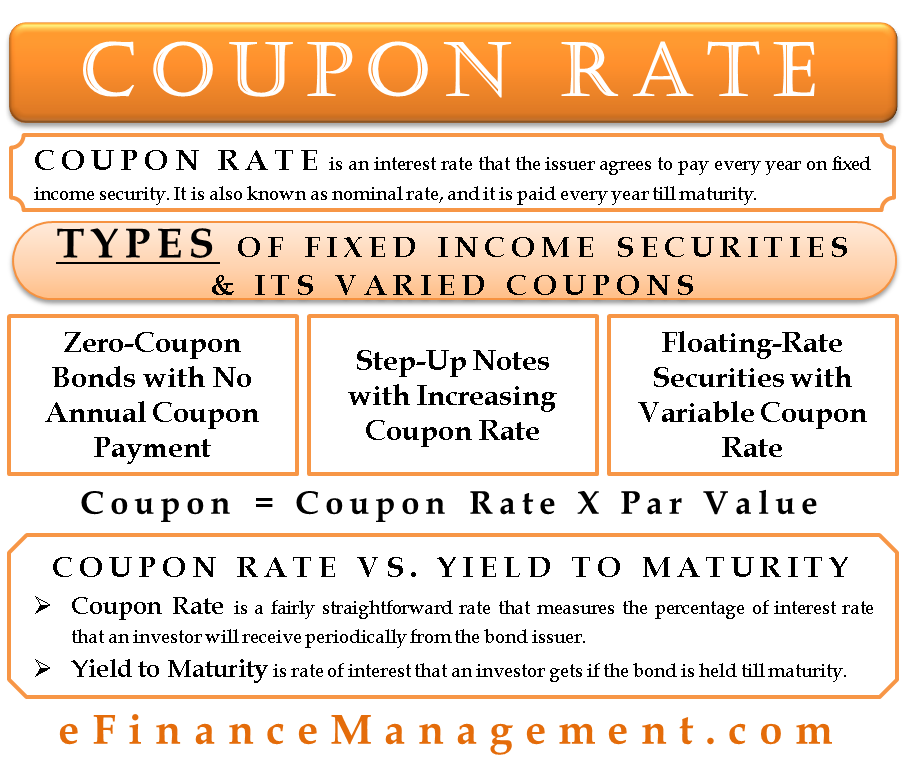
What Is the Coupon Rate of a Bond? - The Balance A coupon rate is the annual amount of interest paid by the bond stated in dollars, divided by the par or face value. For example, a bond that pays $30 in annual interest with a par value of $1,000 would have a coupon rate of 3%.

Coupon value of a bond
[Solved]: 2. Suppose a \( 5 \% \) coupon, 3 year bond is s Suppose a \ ( 5 \% \) coupon, 3 year bond is selling for \ ( \$ 1010 \). The face value is \ ( \$ 1000 \). The coupon is paid every six months. Answer the following questions. (a) Calculate the yield to maturity of this bond. ( 7 marks) (b) Calculate the price of this bond if the yield to maturity increases by \ ( 1 \% \) with maturity ... [Solved]: Consider a bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a YTM of Consider a bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a YTM of 2%, and a face value of $1000. Coupon payments are made semi-annually. The bond matures in 4 years. Trace bond value, current yield, and capital gains yield each year for the bond. Explain what is happening to bond value, current yield, and capital gains yield as the bond reaches maturity. How to Calculate Bond Value: 6 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow to arrive at the present value of the principal at maturity. For this example, PV = $1000/ (1+0.025)^10 = $781.20. Add the present value of interest to the present value of principal to arrive at the present bond value. For our example, the bond value = ($467.67 + $781.20), or $1,248.87.
Coupon value of a bond. Coupon Bond - Guide, Examples, How Coupon Bonds Work A coupon bond is a type of bond that includes attached coupons and pays periodic (typically annual or semi-annual) interest payments during its lifetime and its par value at maturity. These bonds come with a coupon rate, which refers to the bond's yield at the date of issuance. Bonds that have higher coupon rates offer investors higher yields on their investment. Coupon Rate Calculator | Bond Coupon And the annual coupon payment for Bond A is: $25 * 2 = $50. Calculate the coupon rate; The last step is to calculate the coupon rate. You can find it by dividing the annual coupon payment by the face value: coupon rate = annual coupon payment / face value. For Bond A, the coupon rate is $50 / $1,000 = 5%. Bond Price Calculator | Formula | Chart coupon per period = face value * coupon rate / frequency As this is an annual bond, the frequency = 1. And the coupon for Bond A is: ($1,000 * 5%) / 1 = $50. Determine the years to maturity. The n is the number of years it takes from the current moment to when the bond matures. The n for Bond A is 10 years. Determine the yield to maturity (YTM). United States Treasury security - Wikipedia Treasury bills (T-bills) are zero-coupon bonds that mature in one year or less. They are bought at a discount of the par value and, instead of paying a coupon interest, are eventually redeemed at that par value to create a positive yield to maturity.. Regular T-bills are commonly issued with maturity dates of 4, 8, 13, 26 and 52 weeks, each of these approximating a different number of months.
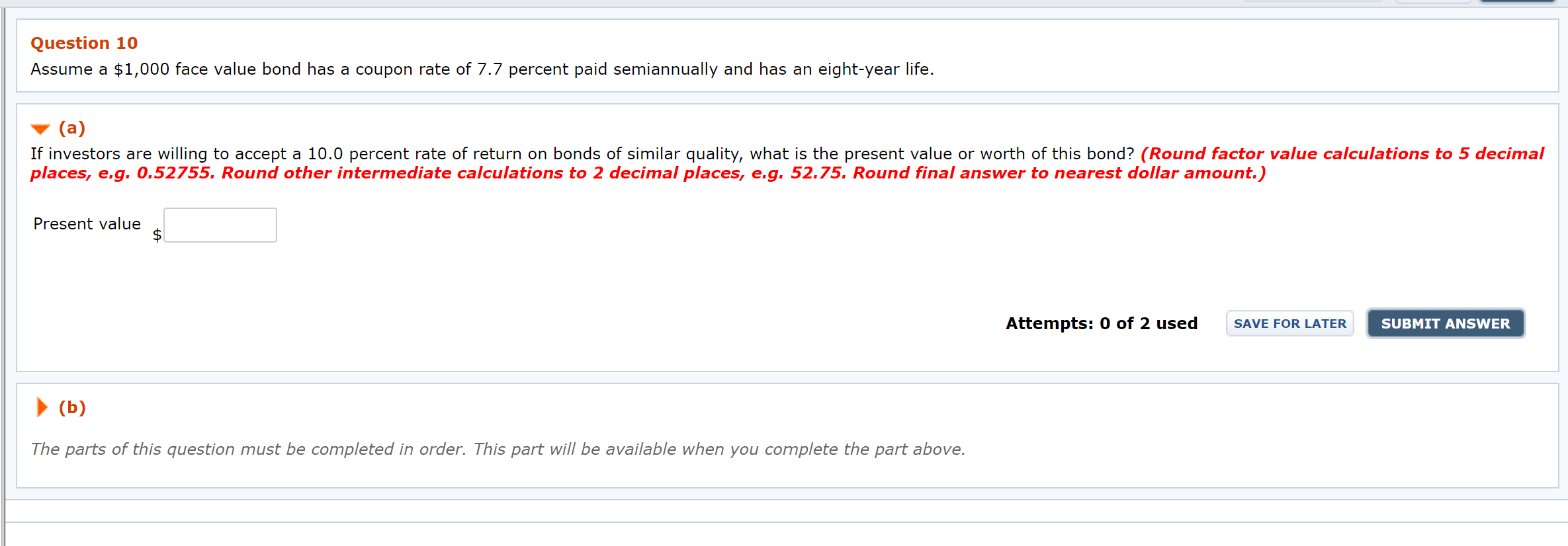
Coupon Rate Definition - Investopedia A bond's coupon rate can be calculated by dividing the sum of the security's annual coupon payments and dividing them by the bond's par value. For example, a bond issued with a face value of $1,000... Suppose a coupon bond with a face value of \( \$ | Chegg.com a. Coupon rate has risen. b. yield to maturity < coupon rate c. yield to maturity > coupon rate d. Coupon rate has declined. Question: Suppose a coupon bond with a face value of \ ( \$ 1,000 \) is currently priced at \ ( \$ 950 \) and has a coupon rate of \ ( 10 \% \). Which of the following is TRUE? What Is a Bond Coupon? - The Balance A bond's coupon refers to the amount of interest due and when it will be paid. 1 A $100,000 bond with a 5% coupon pays 5% interest. The broker takes your payment and deposits the bond into your account when you invest in a newly issued bond through a brokerage account. There it sits alongside your stocks, mutual funds, and other securities. Coupon Rate - Learn How Coupon Rate Affects Bond Pricing The amount of interest is known as the coupon rate. Unlike other financial products, the dollar amount (and not the percentage) is fixed over time. For example, a bond with a face value of $1,000 and a 2% coupon rate pays $20 to the bondholder until its maturity.
25 what is the value today of a 1000 bond 8 coupon i. $ 875.38. Treasury Management - BFI303 27. A Treasury bond has a coupon rate of 9%, a face value of $1000 and matures 10 years fromtoday. For a treasury bond the interest on the bond is paid in semi-annual installments. The current riskless interest rate is 12% (compounded semi-annually). Bond Valuation: Formula, Steps & Examples - Study.com Bond Terms. Horse Rocket Software has issued a five-year bond with a face value of $1,000 and a 10% coupon rate. Interest is paid annually. Similar bonds in the market have a discount rate of 12%. Bond Valuation Overview (With Formulas and Examples) Value of bond = present value of coupon payments + present value of face value Value of bond = $92.93 + $888.49 Value of bond = $981.42. A natural question one would ask is, what does this tell me? When investing, we always hunt for value, whether socks or stocks. We all want to buy something for less than it is worth and sell it for more than ... Answered: Tracer Manufacturers issued a 10-year… | bartleby Tracer Manufacturers issued a 10-year bond six years ago. The bond's maturity value is $1,000, and its coupon interest rate is 6 percent. Interest is paid semiannually. The bond matures in four years. If investors require a return equal to 5 percent to invest in similar bonds, what is the current market value of Tracer's bond?
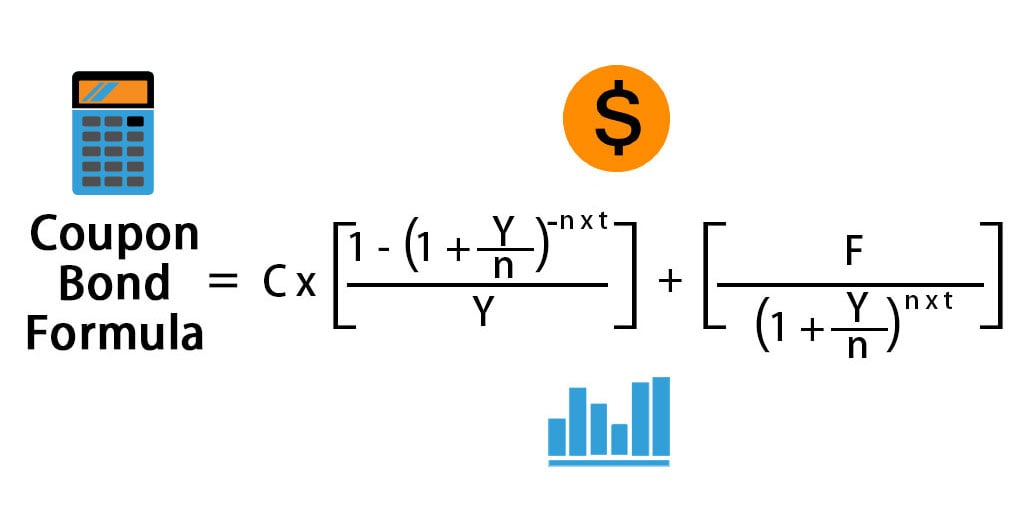
Coupon Bond Formula | Examples with Excel Template - EDUCBA Coupon Bond is calculated using the Formula given below Coupon Bond = C * [1 - (1+Y/n)-n*t/ Y ] + [ F/ (1+Y/n)n*t] Coupon Bond = $25 * [1 - (1 + 4.5%/2) -16] + [$1000 / (1 + 4.5%/2) 16 Coupon Bond = $1,033
What Is Coupon Rate and How Do You Calculate It? - SmartAsset Every six months it pays the holder $50. To calculate the bond coupon rate we add the total annual payments and then divide that by the bond's par value: ($50 + $50) = $100; The bond's coupon rate is 10%. This is the portion of its value that it repays investors every year. Bond Coupon Rate vs. Interest
Coupon (finance) - Wikipedia Coupons are normally described in terms of the "coupon rate", which is calculated by adding the sum of coupons paid per year and dividing it by the bond's face value. For example, if a bond has a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5%, then it pays total coupons of $50 per year.
Bond Price Calculator Let's assume that someone holds for a period of 10 years a bond with a face value of $100,000, with a coupon rate of 7% compounded semi-annually, while similar bonds on the market offer a rate of return of 6.5%. Let's figure out its correct price in case the holder would like to sell it: Bond price = $103,634.84
Coupon Bond - Investopedia Real-World Example of a Coupon Bond If an investor purchases a $1,000 ABC Company coupon bond and the coupon rate is 5%, the issuer provides the investor with a 5% interest every year. This means...
Calculation of the Value of Bonds (With Formula) - Your Article Library Find present value of the bond when par value or face value is Rs. 100, coupon rate is 15%, current market price is Rs. 90/-. The bond has a six year maturity value and has a premium of 10%. If the required rate of returns is 17% the value of the bond will be: = Rs 15 (PVAF 17%6 Years )+110 (PVDF 17% 6 years ), = Rs. 15 x (3.589) +110 (.390)
Answered: K The current zero-coupon yield curve… | bartleby Business Finance Q&A Library K The current zero-coupon yield curve for risk-free bonds is as follows: What is the price per $100 face value of a four-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond? The price per $100 face value of the four-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) Data table (Click on the following icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) 1 3 ...
How to Calculate the Price of Coupon Bond? - WallStreetMojo It determines the repayment amount made by GIS (guaranteed income security). Coupon Rate = Annualized Interest Payment / Par Value of Bond * 100% read more. Example #2. Let us take an example of bonds issued by company ABC Ltd that pays semi-annual coupons. Each bond has a par value of $1,000 with a coupon rate of 8%, and it is to mature in 5 years. The effective yield to maturity is 7%.
Invest in Zero Coupon Bond at Yubi | Learn All About It The formula for calculating the price of a zero coupon bond is: Price of bond = (Face value)/ (1+r)^n, where the face value is the bond's maturity value, r is the imputed interest rate, and n is the number of years to maturity. If the rate of interest is compounded semi-annually, then the formula changes to:
Coupon Rate of a Bond - WallStreetMojo The coupon rate of a bond can be calculated by dividing the sum of the annual coupon payments by the par value of the bond and multiplied by 100%. Therefore, the rate of a bond can also be seen as the amount of interest paid per year as a percentage of the face value or par value of the bond. Mathematically, it is represented as,
How to Calculate Bond Value: 6 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow to arrive at the present value of the principal at maturity. For this example, PV = $1000/ (1+0.025)^10 = $781.20. Add the present value of interest to the present value of principal to arrive at the present bond value. For our example, the bond value = ($467.67 + $781.20), or $1,248.87.
[Solved]: Consider a bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a YTM of Consider a bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a YTM of 2%, and a face value of $1000. Coupon payments are made semi-annually. The bond matures in 4 years. Trace bond value, current yield, and capital gains yield each year for the bond. Explain what is happening to bond value, current yield, and capital gains yield as the bond reaches maturity.
[Solved]: 2. Suppose a \( 5 \% \) coupon, 3 year bond is s Suppose a \ ( 5 \% \) coupon, 3 year bond is selling for \ ( \$ 1010 \). The face value is \ ( \$ 1000 \). The coupon is paid every six months. Answer the following questions. (a) Calculate the yield to maturity of this bond. ( 7 marks) (b) Calculate the price of this bond if the yield to maturity increases by \ ( 1 \% \) with maturity ...
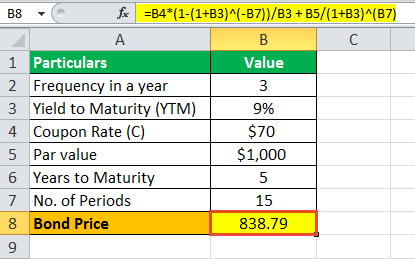
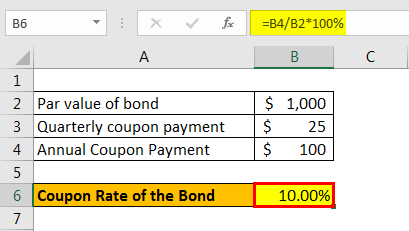



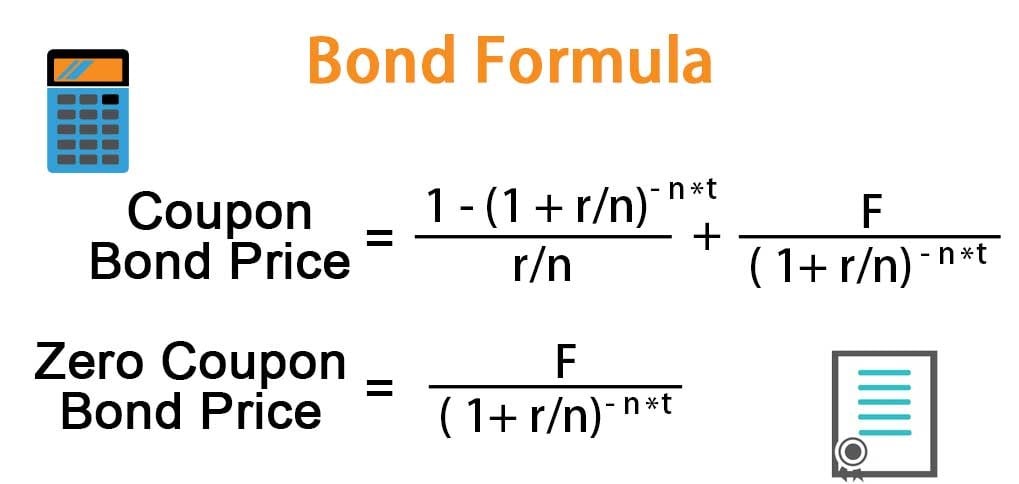
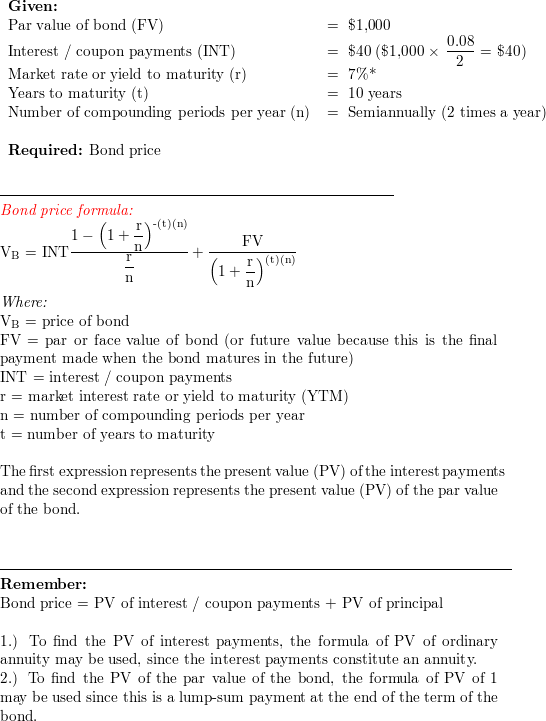



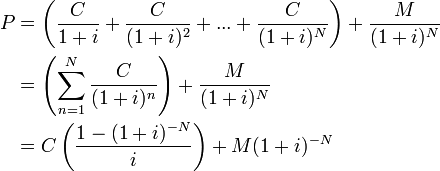

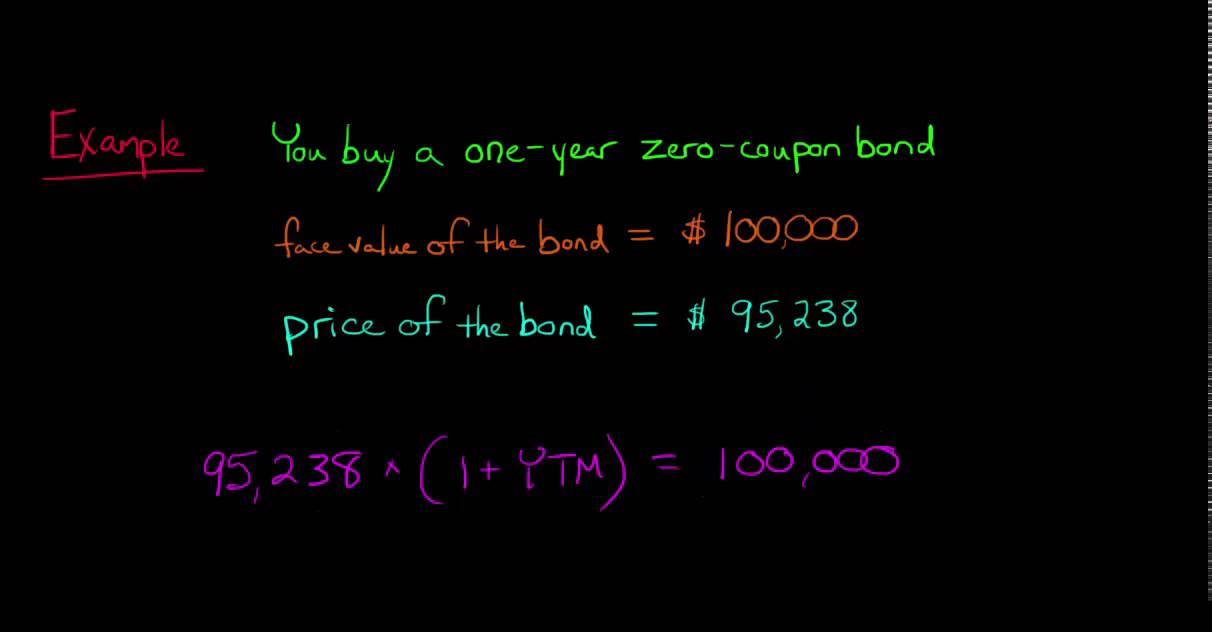




/dotdash_INV-final-How-Can-I-Calculate-a-Bonds-Coupon-Rate-in-Excel-June-2021-01-8ff43b6e77a4475fb98d82707a90fae0.jpg)







Post a Comment for "38 coupon value of a bond"